
The magnitude of binocular gain declines with age 4, 5, 18, 20. This is consistent with reports that binocular summation declines with increasing inter-ocular difference (IOD) in sensitivity and that when IODs are sufficiently large the expectation is that binocular loss, rather than gain, will occur e.g. Studying patients with AMD, which often affects the eyes unequally, Faubert and Overbury 14 and Valberg and Fosse 15 found that approximately half of the patients showed binocular loss. Binocular loss, as used here, refers to worse binocular vision performance than vision performance when viewing with the better eye alone. When the eyes are stimulated unequally as may occur in cataract or following cataract surgery, binocular loss, rather than gain, becomes more likely 6 - 13. For example, Home 3 found more gain for low contrast than high contrast targets, and others have reported that binocular gain is spatial frequency dependent 4, 5. The extent of binocular gain depends on many factors. This gain in performance may reflect probability summation and/or neural summation of the signals from the two eyes 1, 2. IEEE, 1999.Binocular summation (or binocular gain) is the improvement in performance when viewing with both eyes compared to the better eye alone 1, 2. In Computer Vision, The Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on, volume 1, pages 666-673. Flexible camera calibration by viewing a plane from unknown orientations. Journal of the American statistical association, 79(388):871-880, 1984. Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Martin A Fischler and Robert C Bolles.In Computer Vision (ICCV), International Conference on, pages 2564-2571. Orb: an efficient alternative to sift or surf. Ethan Rublee, Vincent Rabaud, Kurt Konolige, and Gary Bradski.In Computer Vision-ECCV 2006, pages 404-417. Herbert Bay, Tinne Tuytelaars, and Luc Van Gool.SVM-Light Support Vector Machine joachims. In Computer Vision-ECCV 2006, pages 428-441. Human detection using oriented histograms of flow and appearance. Navneet Dalal, Bill Triggs, and Cordelia Schmid.Cost of auto crashes and statistics, 2013.Through real word experiments, the system shows a margin of error of 7.5 % in outdoor and long-range conditions. Our approach is not only applicable to measure the distance between vehicles and pedestrians, but, it can be used efficiently to measure the distance to other objects such as traffic signs or animals. In addition, we design a crossover re-detection method to reinforce the robustness of the system.

For that purpose, we use HOG-SVM method to detect pedestrians, and keypoints-based feature extraction method to generate the parallax in a binocular vision system. In this context, the distance estimation problem is investigated in this paper.

In fact, a priori knowledge of the distance between the car and pedestrian allows taking the appropriate decision to avoid collisions.
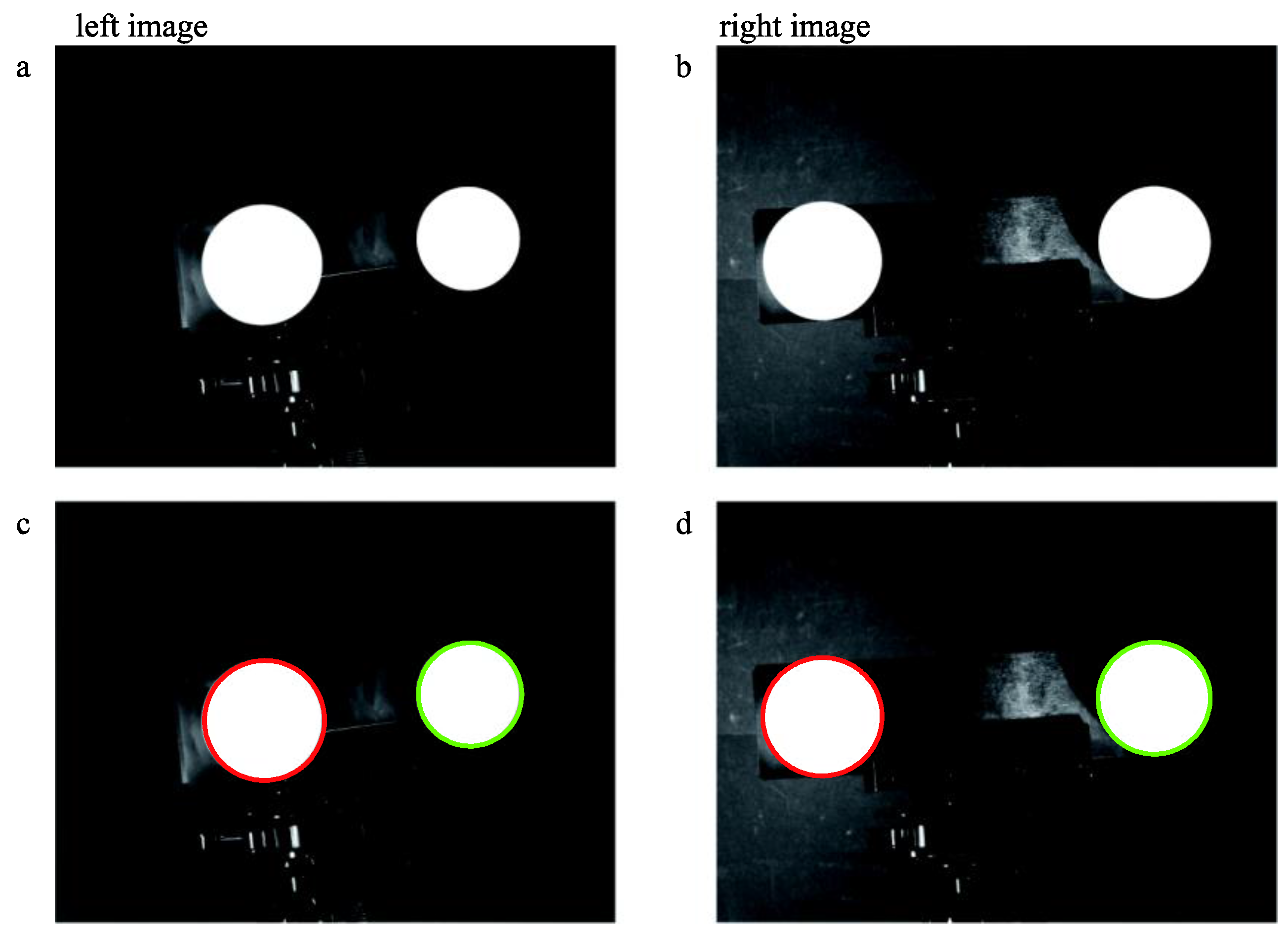
Despite the huge number of research works, many PDSs are designed to detect pedestrians without knowing their precise distances from vehicles. Pedestrian Detection System (PDS) has become a significant research area designed to protect road-users.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
